Understanding ETFs: What Is an ETF?
ETFs can be a great way to potentially capitalize on multiple market movements, indices, or sectors, stocks, or other assets, but what are ETFs exactly, how do they work, what are the different types of ETFs, and how can you trade ETFs?
Here’s what you need to know about ETF trading:
Main Points
- ETFs are investment baskets containing various assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities.
- ETFs can be good for portfolio diversification as they provide exposure to a variety of markets and assets.
- Similarly to stocks, ETFs are trading within stock exchange market hours.
- ETFs can be traded via stock exchanges or through CFDs.
- Some of the main types of ETFs include Commodity ETFs, Indices ETFs, Currency ETFs, Sector ETFs, and Factor ETFs.
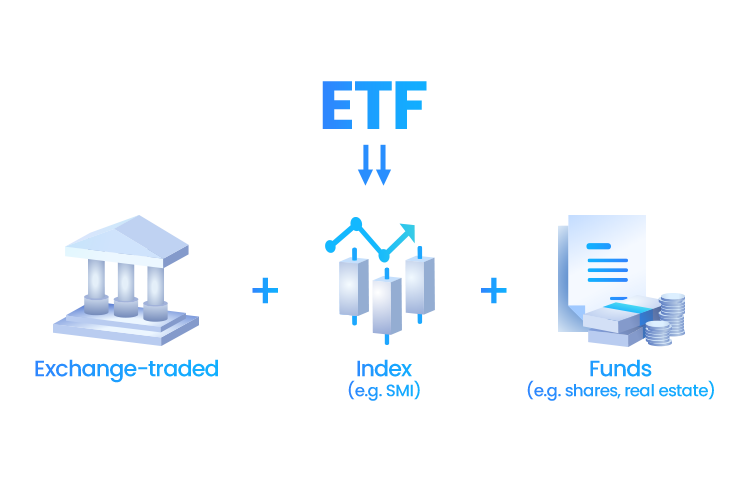
Introduction to Exchange-Traded Funds
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), in simple terms, are baskets of investments that may include a mix of indices, stocks, bonds, commodities, and other assets or markets. ETFs can also track individual assets such as a specific index, commodity, or share.
ETF Basics: How Do ETFs Work
Similar to traditional stock trading, ETFs can be bought and sold (traded) on exchanges, hence the term “exchange-traded.”
In other words, ETFs can be traded on the day the relevant exchanges open.
Furthermore, the prices of ETFs are highly dynamic and can change daily, reflecting the buying or selling activity of the ETF.
ETFs VS. Mutual Funds
Many believe that Mutual Funds and ETFs exhibit similarities since they both represent pooled fund investments.
However, a key difference is that ETFs, unlike Mutual Funds, do not require a fund manager, making them cost-effective.
Additionally, while Mutual Funds can be accessed at the end of the trading day, ETFs can be traded during it (similar to stocks).
Types of ETFs and Their Characteristics
There are multiple types of ETFs and the main ones are as follows:
- Stock ETFs
- Index ETFs
- Sector ETFs
- Bond ETFs
- Commodity ETFs
- Currency ETFs
- Factor ETFs
- Sustainable ETFs
Benefits of Trading ETFs
Some of the benefits of ETFs may be that they are considered to be a good way to diversify one’s portfolio and hedge risk as it can be spread across various financial markets. In addition, ETFs are considered more affordable than mutual funds, and trading them is considered flexible as they are traded when the markets open.
Disadvantages of ETFs
Some of the drawbacks of ETFs may include the fact that they have a lower trading volume and are often subject to capital gain taxes. Additionally, they can sometimes be accompanied by a counterparty risk. This means that one of the parties that participate in the ETF may not carry out their due diligence.
What Moves ETF Prices?
ETF price can be influenced by the prices of the underlying asset or market and by factors like commissions, spreads, trading costs, and operational costs (if applicable).
How to Trade ETFs
ETFs can be traded on stock exchanges like regular stocks. Alternatively, they can be traded as Contracts for Difference (CFDs) with providers like Plus500.
ETF CFDs are derivative contracts between two parties that allow them to gain exposure on rising and falling ETF prices. These contracts are leveraged which may be attractive to those seeking to potentially benefit from price movements. Nonetheless, this also means that it can be more risky as they can multiply their losses.
Find out more about CFD trading by watching our video on. “What Is CFD Trading.”
Common ETF trading strategies
Some of the most utilized ETF trading strategies include short-selling and swing trading:
Short-Selling ETFs
Shorting or Short-Selling refers to the act of selling an ETF if they believe the price will fall and then buying it at a lower price. In case the prices go along with one’s predictions, then Shorting can be quite successful. You can read more about Shorting in our “What Is Short Selling” article.
Swing Trading ETFs
Simply put, Swing Trading is a strategy that attempts to incur profit from the initiation and then the exiting of a position on ETFs in a short period by attempting to capitalize on price “swings.”
ETF Trading Hours
ETFs are traded at the same time Stock Exchanges Open. So, for example, US ETFs are traded from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST.
FAQs
What exactly is an ETF and how is it different from a stock?
An Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a pooled investment fund comprised of a basket of assets like bonds, stocks, and commodities, among others.
How do ETFs work in the stock market?
ETFs pool capital from investors from a group of assets.
What are the main types of ETFs available?
Some of the main types of ETFs include Commodities ETFs, Indices ETFs, Stocks ETFs, Bonds ETFs, and Currency ETFs.
Are there any risks involved in ETF trading?
Although ETFs are generally considered lower-risk investments, they are still accompanied by some risks like tax risk, liquidity risk, and counterparty risk.
How are ETFs priced and traded throughout the day?
ETF prices are dynamic and fluctuate often based on the buy and sell prices of the underlying asset.
Can ETFs be used for short-term trading strategies?
Yes, ETFs can be used for short-term trading as well as long-term trading and investing.
